Economic order quantity (EOQ) is the ideal quantity of units a company should purchase to meet demand while minimizing inventory costs such as holding costs, shortage costs, and order costs. This production-scheduling model was developed in 1913 by Ford W. Harris and has been refined over time.
It strikes a balance between ordering costs and holding costs, ensuring businesses operate efficiently without unnecessary expenses. In this video, we will explore the EOQ formula, its components, importance, and Limitations.
What you are going to learn?
Importance of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Across Industries
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a crucial inventory management concept that helps businesses optimize order sizes, control costs, and maintain efficiency. Whether in manufacturing, retail, healthcare, or construction, EOQ ensures smooth operations by balancing inventory levels and minimizing waste.
Cost Control:
EOQ helps businesses determine the ideal order quantity, preventing excessive bulk purchases and reducing storage costs. This ensures that capital is not unnecessarily tied up in inventory, improving overall financial efficiency.
Avoiding Stock Shortages:
Maintaining a steady supply of materials or products is essential in every industry. EOQ ensures timely replenishment, preventing shortages that could disrupt production, sales, or service delivery, thereby avoiding delays and revenue losses.
Efficient Inventory Management:
Companies dealing with large volumes of raw materials, finished goods, or supplies benefit from EOQ by balancing order frequency with storage capacity. This optimizes warehouse space, reduces carrying costs, and improves inventory tracking.
Improved Cash Flow:
Ordering the right quantity of materials prevents excess inventory accumulation, allowing businesses to allocate funds to other critical areas such as expansion, innovation, or unexpected expenses.
Reduced Waste and Sustainability:
Over-ordering leads to excess stock that may become obsolete, expire, or go to waste, increasing disposal costs and environmental impact. EOQ promotes sustainable resource use by ensuring optimal procurement practices.
Graphical Representation of EOQ
Economic order quantity (EOQ) graph.
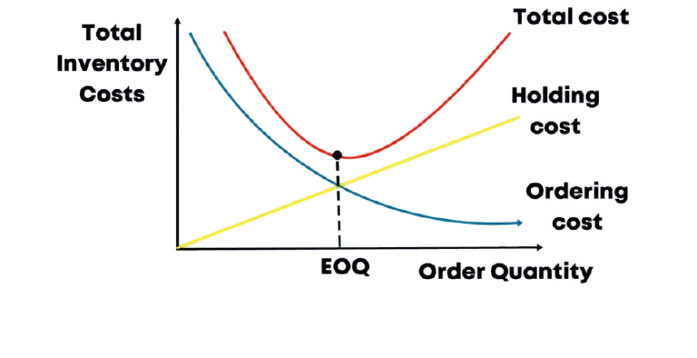
The EOQ graph typically displays these costs as follows:
- X-axis (Horizontal): Order Quantity (the number of units ordered).
- Y-axis (Vertical): Total Inventory Costs.
- Holding Cost Curve: This line slopes upward, indicating that holding costs increase as the order quantity rises.
- Ordering Cost Curve: This line slopes downward, showing that ordering costs decrease as the order quantity increases (because fewer orders are placed).
- Total Cost Curve: This is a U-shaped curve, representing the sum of holding costs and ordering costs.
- EOQ Point: The lowest point on the total cost curve. This point signifies the optimal order quantity where total inventory costs are minimized.
The formula for Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The formula for EOQ is:
EOQ = square root of 2DS/H.
Where:
D = Demand in units, typically for a year.
S = cost of each order.
H = Holding cost per unit per year.
This formula helps businesses determine the most cost-effective order quantity.
Understanding EOQ with an Example
Let’s assume a company sells 10,000 units of a product annually. The cost of placing an order is $50, and the holding cost per unit per year is $2.
Using the EOQ formula:
EOQ= square root of (2×10000×50)/2 = 707.1
This means the company should order approximately 707 units per order to minimize costs.
Key Components of EOQ
To understand EOQ better, let’s break down its components:
1. Ordering Costs
Ordering costs include all expenses related to placing and receiving an order. These costs typically cover administrative expenses, supplier communication, and logistics.
2. Holding Costs
Holding costs are incurred for storing unsold inventory. These costs include warehousing expenses, depreciation, insurance, and obsolescence risks.
3. Demand Rate
The demand rate represents the consumption rate of the product over a specific period. It is crucial to estimate demand accurately to maintain an optimal inventory level.
Practical Applications of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
While EOQ is often introduced as a theoretical concept in academic settings, its true power lies in its wide-ranging real-world applications across various industries. Whether managing a small business or operating a complex global supply chain, understanding and applying Economic Order Quantity can significantly optimize inventory management and reduce operational costs.
Here’s a deep dive into how EOQ plays a crucial role in different business scenarios:
1. Retail Inventory Optimization
Retailers constantly face the challenge of maintaining the right stock levels. Overstocking ties up capital and storage space, while understocking leads to lost sales and dissatisfied customers. EOQ helps strike a balance by determining the most cost-effective quantity to reorder.
For example, a bookstore can use EOQ to decide how many copies of a popular title to order at once, factoring in storage limitations and reorder costs.
2. Manufacturing and Production Planning
In manufacturing, EOQ isn’t just about ordering raw materials, it’s about aligning procurement with production cycles. By calculating EOQ, manufacturers can ensure that materials arrive just in time to meet production schedules, minimizing idle time and avoiding material shortages. This is especially critical in just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing systems, where efficiency and timing are everything.
3. Healthcare and Pharmaceutical Inventory
Hospitals and pharmacies rely on EOQ to maintain critical inventory levels without overstocking perishable or high-cost medications. EOQ models help in planning the procurement of medical supplies like gloves, syringes, or commonly used drugs, ensuring they are always available but not in excess, thereby preventing wastage due to expiration.
4. E-commerce and Fulfillment Centers
In the age of rapid delivery and fluctuating demand, e-commerce businesses must carefully manage stock levels across multiple warehouses. EOQ helps these businesses decide how much of each product to reorder and reduces the risk of stockouts during peak seasons while avoiding unnecessary holding costs. Integration of EOQ into automated inventory systems further streamlines the process.
5. Agriculture and Perishable Goods
Farmers and food suppliers use EOQ to manage perishable items such as fruits, vegetables, or dairy products. Since holding time directly impacts quality, EOQ helps minimize storage duration while maintaining sufficient supply. Seasonal factors and spoilage rates are often incorporated into the EOQ model for better accuracy.
6. Automotive Spare Parts Management
For automobile companies and service centres, stocking the right quantity of spare parts is crucial. Too few, and customers have to wait; too many, and valuable shelf space and capital are wasted.
EOQ aids in determining optimal reorder quantities based on demand frequency, part cost, and holding cost, especially useful in managing slow-moving but essential inventory.
7. Construction and Real Estate Projects
Large-scale construction projects often require materials in bulk. However, storing too much material on-site can lead to losses through damage or theft. EOQ can guide procurement teams to order in appropriate quantities and schedules, ensuring materials arrive when needed without unnecessary surplus.
8. Government and Defense Supply Chains
EOQ is also used in the public sector, particularly in defence logistics where timely availability of equipment, uniforms, and consumables is vital. Using EOQ models helps manage taxpayer funds efficiently while ensuring readiness and operational capability.
9. Sustainable Inventory Practices
EOQ can contribute to sustainability goals by minimizing overproduction, waste, and carbon emissions associated with excessive storage and frequent transportation. Businesses adopting green logistics are increasingly tweaking EOQ formulas to include environmental costs, turning EOQ into a tool not just for economic savings but for eco-efficiency as well.
10. Tech and Electronics Industry
Tech companies deal with high-value, fast-depreciating inventory. EOQ helps manage the procurement of components like processors, memory chips, and other hardware in a way that aligns with fast product cycles and innovation demands. This ensures components are not rendered obsolete while in storage.
Limitations of EOQ
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model operates under the assumption that consumer demand remains steady. It also presumes that ordering and holding costs do not fluctuate.
However, these assumptions present limitations, as the EOQ formula does not effectively accommodate real-world business scenarios. Factors such as fluctuating consumer demand, seasonal variations in inventory expenses, potential revenue loss from stock shortages, and bulk purchase discounts are not accounted for in the standard EOQ calculation.
As a result, businesses may find it challenging to rely solely on this model for inventory management.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) remains a cornerstone of efficient inventory management. By minimizing costs and optimizing order quantities, businesses can enhance profitability and streamline their supply chain operations.

