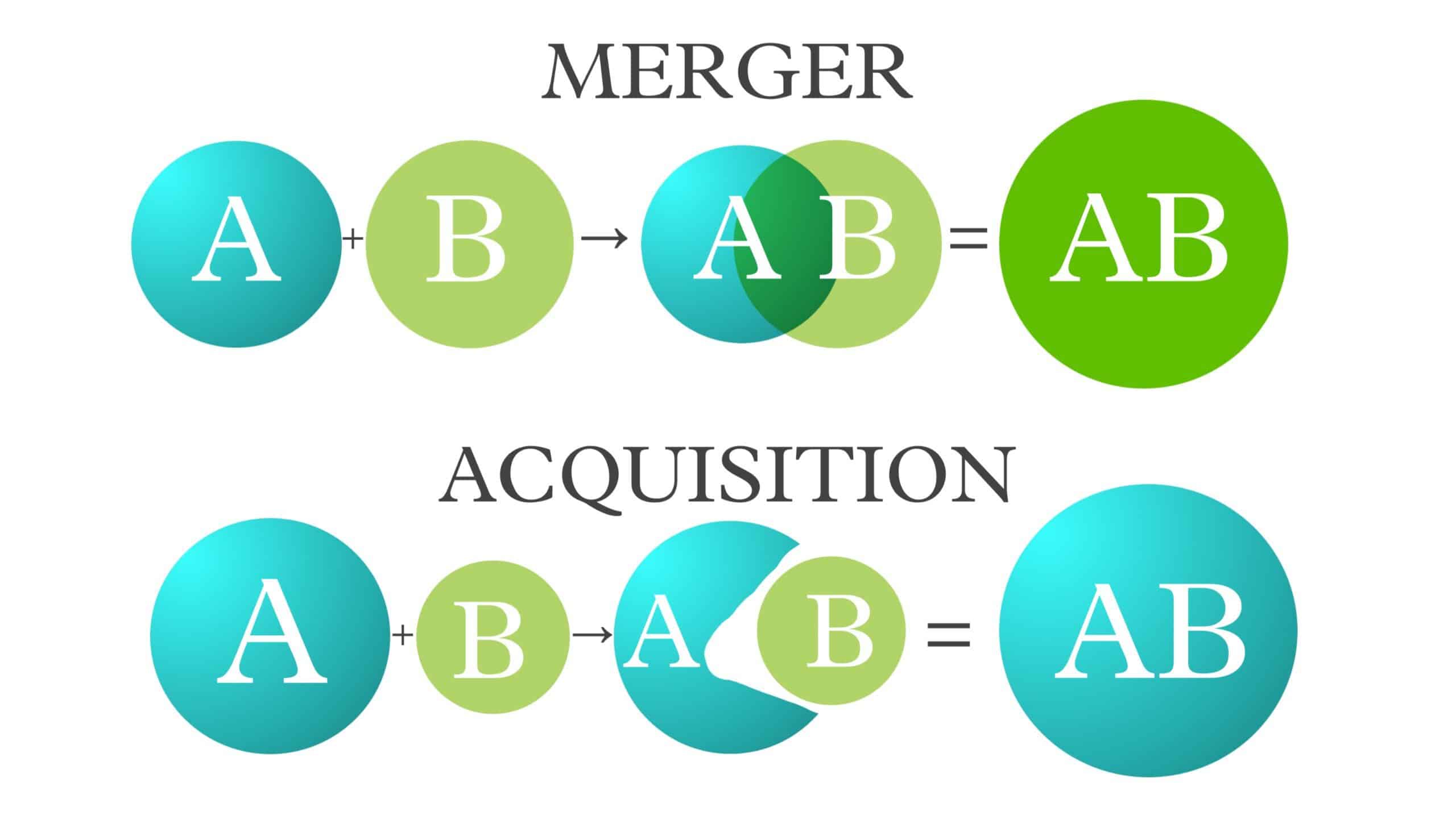
Mergers and acquisitions are transactions of shifting ownership between two companies, wherein a merger is a fusing or combining of two companies and acquisition is one company acquiring or buying another. The ultimate goal of mergers and acquisitions is to create synergy, which typically makes the two combined companies worth more valuable than the two separate companies.
It involves privately held companies that entail several key legal, business, human resources, intellectual property, and financial issues. It is helpful for understanding the dynamics and issues that frequently arise within your company.
What you are going to learn?
What is Merger?
Definition:
A merger is a corporate strategy of combining or fusing two separate companies into a single company in order to enhance financial and operational strengths.
Two companies can start a merger by having the board of directors accept and seek shareholders’ permission for combining two separate companies into one company. Here, both companies should be of comparable size. Sometimes, this process creates an entirely new company.
There are mainly two concepts in a merger:
- Acquiring Company: The company which purchases the majority of equity shares of other company.
- Acquired Company: It sells its most of the shares to the acquiring company.
5 Types of Mergers
Generally, there are 5 types of company mergers; horizontal merger, vertical merger, conglomerate merger, market extension merger, and product extension merger.
Let’s talk about these mergers:
Horizontal Merger
A merger that occurs between companies in the same field, often as competitors offering the same product or service.
This type of merger is common in industries with fewer firms, as competition is stronger and the synergies and potential gains in market share are much higher for merging firms in such an industry.
Example: for example, the merger between two-wheeler giant Hero and Honda was horizontal in nature. The objective of this merging was to make reliable and budget-friendly bikes for Indians.
Vertical Merger
A merger occurs between two companies that produce different products or services for a single finished product.
The logic behind this merger is to increase synergies created by merging companies for more efficient operating.
Example: For example, a company which makes engines for cars and another company which makes the body of a car. The merger of these two companies is considered a vertical merger.
Conglomerate Merger
This type of merger happens between the firms involved in completely unrelated business activities. Conglomerate mergers can be classified into two types; mixed and pure. Mixed conglomerate mergers involve the firms that are looking for market extensions or product extensions, while pure conglomerate mergers involve firms that have nothing in common.
Example:
Walt Disney Company & American Broadcasting Company merger is the prime example of a conglomerate merger.
Market Extension Mergers
This type of merger happens between two businesses that deal with the same products but in different markets. This merger gets access to a bigger market and makes a bigger client base.
Example: The perfect example of market extension mergers was when RBC Centura (Royal Bank of Canada) acquired Eagle Bancshares. The main purpose of this deal was to access the market in North America. Besides that, the Atlanta financial market (Headquarter of Eagle Bancshares) was the leader in the banking world, which made this deal a great opportunity for RBC.
Product Extension mergers
A product extension merger takes place between two companies that deal in the products and services that are related to each other and operate in the same market. It allows the companies to group together with their products and get access to a huge amount of consumers.
Example: A good example of a product extension merger was the merger of Pizza Hut and PepsiCo in 1977.
What is Acquisition?
Definition:
An acquisition is a corporate transaction where one company purchases one portion or all shares and assets of another company.
The primary motivation behind the acquisition is to take control of the target company’s strengths and capture synergies.
The acquisition allows the acquiring company to make decisions concerning the acquired assets without needing the approval of shareholders of the target company.
Types of Acquisitions
Here, the types of acquisitions are classified based on the businesses of companies involved.
Horizontal Acquisition
When a company acquires another company in the same business or industry, that is called horizontal acquisition. After this type of acquisition, the acquired company still exists with its brand name, but that is owned by the acquiring company.
Example: These days the social media giants are Facebook, WhatsApp, and Instagram. Facebook acquired WhatsApp and Instagram, But still, these both exist with their brand name, however, these are now owned by Facebook. this is a perfect example of a horizontal acquisition.
Vertical Acquisition
When a company acquires either a supplier of inputs or a distributor of its products or the company to which it sells its products, that is called vertical acquisition.
The primary motive of this acquisition is to have higher control over the supply chain and therefore impacting the receipt of raw material and delivery of the product to the ultimate user.
Example: Google gained the smartphone producer Motorola in 2012.
Conglomerate Acquisition
To introduce diversification, when a company acquires another company with a completely different kind of business or service.
Example: Recently, Reliance Industries took over Hamley’s, a toy company to introduce diversification. This is an example of Conglomerate Acquisition.
Congeneric Acquisition
When two companies share similarities, come together, that is called Congeneric Acquisition. Similarities can be anything, either similar distribution channels, or similar production technologies, and so on, but the production activity of the two companies is not related.
Example: The proper example of congeneric acquisition is when banking giant Citicorp acquired the financial services company Travelers Group in 1998.
Forms of Acquisition
Generally, there are two forms of acquisition- stock purchase and asset purchase.
Stock Purchase
In a stock purchase, the acquiring company pays cash or shares to the shareholders of the target firm for the shares of the target company. Here the target company’s shareholders receive compensation.
In this case;
- The acquirer company takes all the assets and liabilities from the target company.
- Shareholders must approve the transaction through a majority vote to receive the compensation by the acquirer. This can be a long process.
- Shareholders bear tax responsibility as they receive the compensation.
Asset Purchase
Asset purchase means the acquirer purchases the target company’s assets and pays the target directly.
Here;
- The acquirer will avoid assuming any of the acquired company’s liabilities, as it purchases only the assets.
- In this purchase, no shareholder approval is needed unless the assets are significant.
Methods of Payment in mergers and Acquisitions / M&A Transactions
There are basically two methods of payment – cash, stock, and bond. Sometimes M&A transactions use a combination of cash and stock, which is called a mixed offering.
Cash
In this method, the acquirer pays cash for the target company’s shares. For its simplicity and transparency, this method is used broadly all over business domains, but it drops its relevancy when the transaction costs are too high.
Stock
In the stock offering method, the acquirer company issues new shares that are paid to the target company’s shareholders.
Bond
In this type of payment method, the acquiring company issues a corporate connection to buy shares and assets of the target company. It required a huge credit rating and negotiability.
Benefits of Mergers and Acquisitions
There are some common reasons for mergers and acquisitions, such as it allows enterprises to grow and change the nature of their businesses. Merger & Acquisition opens a room full of opportunities for a company, such as;
Unlocking Synergies
The most common goal of M&A is to create synergies, in which the merged company is worth more than two individual companies.
Cost synergies are created due to economies of scale (which is discussed below) and revenue synergies are created by increasing market share, higher prices, and cross-selling.
Economies of scale
When two companies merge together, it becomes more potent with abundant resources. After merging, the newly developed company will get access to a more skilled workforce that will help in increasing its scale of operations. Economies of scale will occur when a company uses its resources efficiently and has an optimum distribution of networks, research, and development facilities.
Higher Growth
Mergers and acquisitions are the faster ways for a company to get higher revenues as compared to growing organically and individually.
Diversification of Products and Services
One of the most significant reasons for M&A is to introduce diversification into the products and services of a company. Sometimes it reduces the risk of failure as it facilitates a company to merge with a company that is already established. It also allows the former to explore new business operations.
Eliminations of Competition
M&A of two or more companies eliminate competition in an industry. It saves the advertising cost of the company, and it enables the merged company to reduce the cost of its products and services. It will also favor the customers since they will get the products at lower prices.
Stronger Market Power
The merged or acquired companies will attain a higher market share and will gain the power to manipulate prices due to cost-cutting.
Best Financial Planning
When one or more companies decide for a merger or acquisition, they can plan to utilize their resources in the best possible way. The funds and finances of a merged or acquired company will be more and their utilization may accordingly be better than in the separate units.

4 thoughts on “What are Mergers and Acquisitions? M&A Definition, Example, Types, Forms, and Transactions”