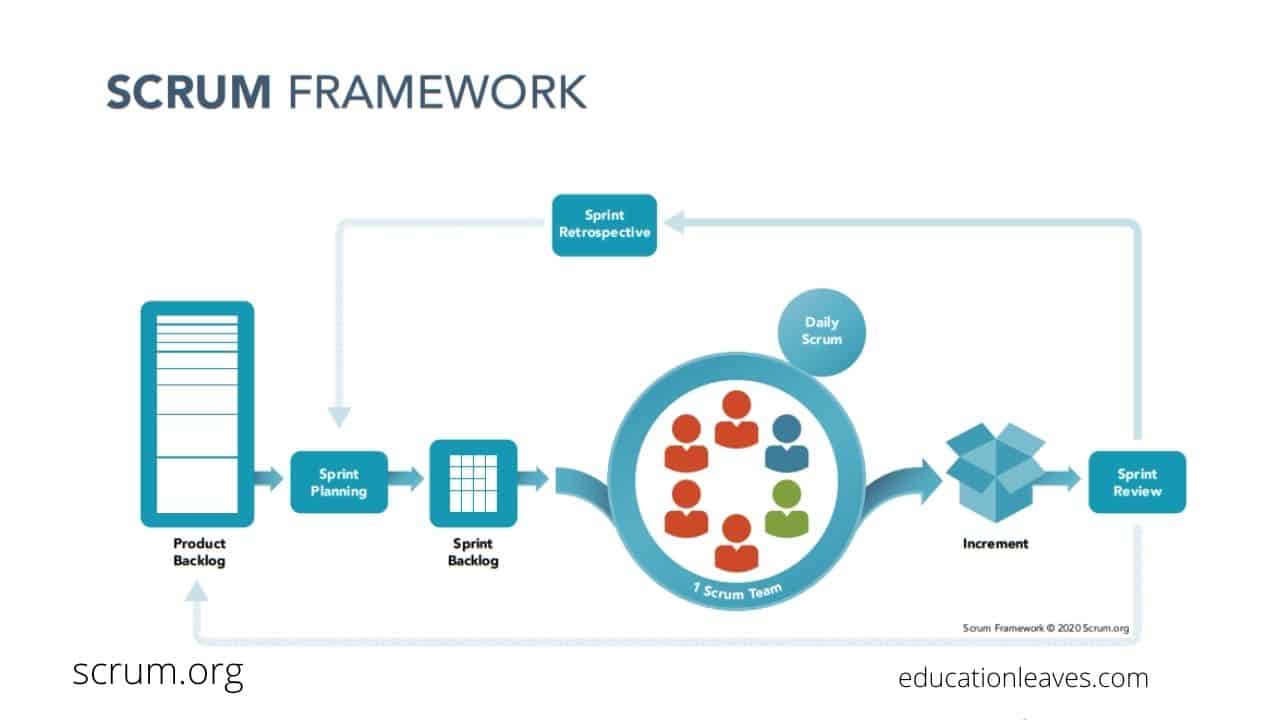
A scrum is an iterative method, consisting of sprints that normally last 1 to 4 weeks. This method ensures that your team provides a version of the product regularly. it was created using a software model that follows a set of functions, duties, responsibilities, and meetings.
It is a software development based project management framework.
Scrum can be operated for any complex project but performs best when the outcome is a concrete product rather than a service.
What you are going to learn?
Definition of Scrum
Scrum is a framework for project management that highlights collaboration, teamwork, responsibility, and iterative progress toward a well-defined goal.
or
Scrum is a framework that allows people, teams, and organizations to develop value through adaptive solutions for complex problems.
or
Scrum is a framework of practices, rules, roles, vents, and artifacts used to execute agile projects.
Roles in Scrum
If an organization adopts Scrum, the first thing to understand is how Scrum roles are different from standard project management roles. There are mainly three roles in Scrum- Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Scrum Team. Let’s start with a brief discussion of each of these.
1. Product Owner
The product owner is a scrum role for a person who represents the business or user community. The product owner is responsible for working with the user group to decide what features will be in the product release. Here are some important responsibilities of the product owner:
- Explain customer needs to the development team,
- Collect manage, and prioritize the product requirements,
- Manage profitability,
- Take over any responsibilities related to the product or service when needed,
- Set the market release date of the specific product or service,
- Responsible for product backlogging.
2. Scrum Master
A scrum master is a facilitator for an agile development team. The scrum method allows a team to self-organize and perform changes quickly, under agile principles. The scrum master deals with the process of how information is exchanged.
Here are some responsibilities of a Scrum Master:
- To perform as a coach,
- Teach the team to follow scrum values and practices,
- To protect the team from external conflicts,
- To promote cooperation between the stakeholders and the team,
- Secure the team from any organizational distraction.
3. Scrum Development Team
The development team is made of 5-9 people who satisfy all the technical needs to deliver the product or the service. The Scrum team is like the car itself, ready to go along in whatever path it is directed. The product owner makes sure that the car is always going in the appropriate direction. And the Scrum master is the mechanic, maintaining the car, and performing at its best.
Now let’s discuss some responsibilities of the development team:
- Responsible for creating a ‘done’ increment at the end of each sprint,
- Picking up the items from the prioritized product backlog,
- Create tasks by breaking down the sprint items,
- Providing estimates to the sprint items.
3 Pillars of Scrum
Every scrum team must work with a few principles- transparency, inspection, and adaptation. These are called the three pillars that hold scrum together.
![What is Scrum? [PDF] Definition, Roles, Pillars, Events, Artifacts, Advantages & disadvantages](https://educationleaves.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Scrum-pillars.png)
Let’s discuss these principles:
1. Transparency
Transparency means giving visibility to the significant aspects of the process to those responsible for the outcome.
Meaning of transparency consists of:
- Free and easy flow of information between team members,
- A common mission and vision for the team,
- A common language for all,
- regular meetings for all team members
2. Inspection
Timely checks on the progress toward a sprint goal to detect undesirable variances are called inspection. In a scrum team, everyone is involved in the development inspection process. Inspection is not possible without transparency.
In inspection, we generally inspect:
- The process,
- The tools,
- The artifacts,
- The product,
- The people involved in the whole process,
3. Adaptation
Adaptation is the pillar that has the most effective impact on the product. It means adjusting a process as soon as possible to minimize any further modification issues.
Scrum Events
Scrum events are some ceremonies that foster team collaboration and make sure that there is a constant line of communication among the scrum team members through the software development life cycle or the product.
Before we jump into the scrum events, first, we should know about “Sprint”. Sprint is considered the basic unit of work for a scrum team. It is the feature that makes a distinction between scrum and other frameworks for agile development.
now let’s discuss some of the scrum events:
1. Sprint Planning
Using the product backlog, teams start with the highest priority items and determine how to reach this aim. A good tip when sprint planning is to do the due intensity and only start with items that are ready.
Planning is also a quick and short process, so don’t get bogged down in the details. Just get to work on meeting the targets. Put the plan collaboratively. The team should also question the product owner and stakeholders.
2. Daily Scrum Meeting
It is a short meeting that happens daily during the sprint period.
The main objective of the daily scrum meeting is to evaluate the progress and trend until the end of the sprint and to create a new plan for the next 24 hours.
In a daily scrum meeting, three questions are answered individually;
- What did I do yesterday?
- What I’m going to do today?
- What help do I require?
3. Sprint Review
The main objective of the sprint review is to review the completed work regarding the product backlog for future deliveries. From the review, you can take the necessary information and apply that to future sprints to reflect the positives and eliminate the negatives.
This process begins by thanking the participants, offering brief introductions, and setting ground rules for the discussion.
4. Sprint Retrospective
This is a discussion on the last sprint and figuring out what went well and what went wrong. Customer and stakeholder feedback is also gathered and discussed in order to prioritize user stories and improve product quality and performance.
Scrum Artifacts
In the Scrum framework, the term artifact relates to the key concepts that are used by the scrum team to produce products in an agile environment. Here are some main artifacts that every scrum team needs;
1. Product Backlog
A product backlog is the list of everything that a product needs to satisfy the customer’s needs. It is prepared by the product owner and reviewed by the scrum master. A product backlog is prioritized according to what is more and what is less important for the organization.
2. Sprint Backlog
The sprint backlog is a subset of items of the product backlog that is selected by the team to perform during the sprint. The sprint backlog is displayed on physical boards called the scrum board. This board makes the development process transparent for everyone.
3. Product Increment
It refers to all the product backlog items that have been completed during a sprint. It is also used to represent the sum of all the completed backlog items and user stories.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Scrum
There are some reasons scrum is so popular today;
- Scrum helps teams complete project deliverables efficiently.
- It fosters effective utilization of money and resources.
- It allows a larger project to divide into small and manageable sprints.
- Developments are checked and coded during the sprint review.
- The development team gets clear visibility in scrum meetings.
- It adopts feedback from stakeholders and customers.
Now let’s discuss some disadvantages of scrum;
- Because of the lack of a definite deadline, sometimes scrum leads to scope creep.
- Without proper commitment and cooperation, the chances of failure become high.
- It is challenging to adopting scrum in large teams.
- Sometimes, daily meetings are frustrating for the team members.
- If someone leave the project in the middle, the entire project can collapse.
Download Scram PDF
Related topics