Distribution Channel or Channel of Distribution [PDF Included] Definition, Types, Functions, Benefits, and Drawbacks
With any business, specifically an e-commerce business, there are many facets to being successful. Understanding everything from marketing to logistics will help you stand apart from the crowd.
In this article, I’ll discuss everything about distribution channels.
‘Distribution’ means the allocation of something to its recipients. Therefore, the term, ‘distribution channel’ refers to the various paths used for the purpose of distribution of something.
What you are going to learn?
Definition:
The path taken by the goods or services when they move from the manufacturer to the end consumers is called a distribution channel.
Or
The channel of distribution is the path that a product and service take on their way from the manufacturer or provide to the end consumer.
Or
A channel of distribution is the path used to get a product from the manufacturer or service provider to the end user.
Or
A route through which a product travels from the production end to the point of consumption is called a distribution channel.
The distribution channel includes a manufacturer, a wholesaler, a retailer, the internet, and the consumer. It can also provide a sense of how money flows back from the buyers to the producer. The transfer of goods implies the transfer of ownership.
It is a network of intermediaries who carry out several interrelated and coordinated functions in the flow of goods from their origin to their destination.
How Does Distribution Channel Works In Business?
The main objective of a business is to bring its product or service to the market and make it available to consumers. This movement of products between the manufacturer and the consumer takes place through a distribution channel. The manufacturers decide whether they want to deal with the consumers directly or they would like to appoint intermediaries to reach the end consumers.
Some businesses set up their own distribution units or retail stores to deal with the consumers directly. Some businesses prefer middlemen (wholesalers, retailers) to deliver their products to consumers.
An effective distribution system involves using network resources and logistics to their full potential at the lowest possible cost. The decision to appoint the perfect distribution channel for products depends on several factors, such as the cost of distribution, product type, sales goals, and the targeted market.
As multiple channels make the product reach the customer easily, it also increases the price of the product, which directly affects the brand’s position in the market.
A business must learn about its target customers’ presence in the market, acquire new customers, and build up customer loyalty. So a manufacturer should be cautious when adopting a distribution channel to increase sales revenue while reducing market risk.
Example of Distribution Channel
There are multiple healthcare companies have come up with vaccines to fight the Coronavirus. But they cannot reach the public directly or keep track of people who are vaccinated or non-vaccinated. So, they gave those vaccines to the central and the state government. Then the government distributed those vaccines to multiple vaccination centers. A centralized database manages details of the people who visited those centers and got vaccinated.
Types of Distribution Channel
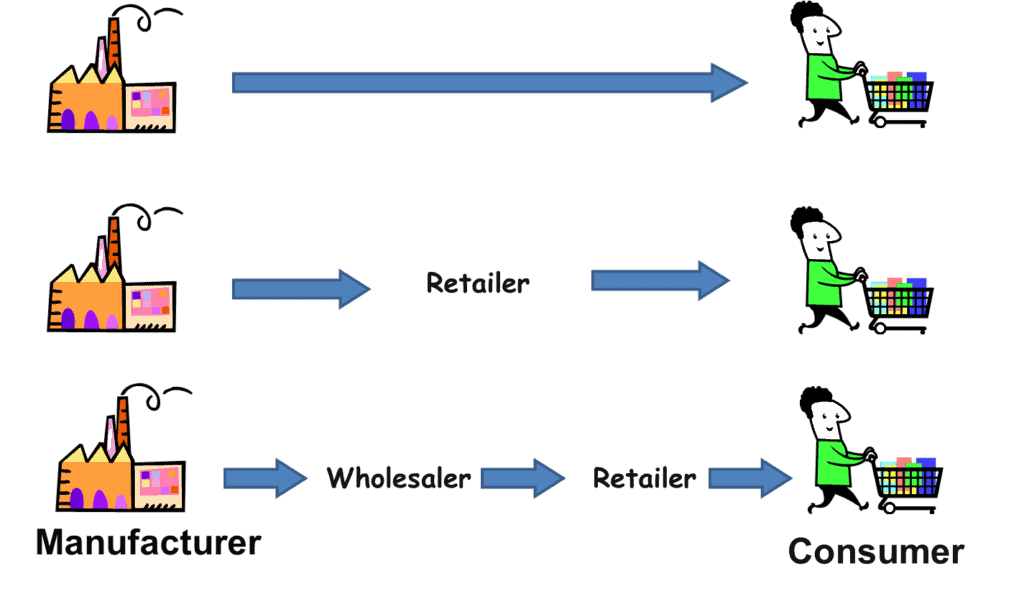
There are mainly two types of distribution channels;
1. Direct channel:
To reach the hands of the customers, products, and services pass through various hands. But there are some manufacturers who sell their products directly to their customers. This type of distribution channel is called a direct channel.
No middleman exists in the case of the direct channel. The manufacturer supplies its products to the consumers through its own retail store, salespeople, and their own delivery system. This system is known as a Zero Level Channel.
- Manufacturer↣ End Consumers
Examples: Consultancy Companies, Jewelries, Car companies, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Direct Channel:
Here are some advantages of direct distribution channels;
- The direct distribution channel gives businesses total control over how their product is marketed and sold.
- It allows a brand to build genuine relationships with the end users.
- Direct channel ensures e-commerce consumers’ satisfaction with the speedy delivery of products.
- It eliminates the cost of hiring intermediaries.
- It allows companies to distinguish themselves from their competitors.
- It allows companies to collect data regarding their customer’s buying habits, demographics, and other important information directly.
Besides several advantages, there are some disadvantages too;
- It requires warehouse management to deal with the inventory.
- Businesses with direct distribution channels miss the opportunity to widen their reach.
- Setting up its own warehouses, showrooms, and delivery system can be cost-sufficient and time-consuming.
2. Indirect Channel
When a company manufactures products on a large scale, it is challenging to make direct selling of products to the consumers. Here, the middleman is introduced into the business to make sure the availability of the products to its consumers. It may involve mercantile agents, wholesalers, and retailers.
Examples: supermarket chain, crop, food, beverage, etc.
Types of Indirect Channels:
There are mainly three types of indirect distribution channels;
- One-Level Channel: It means a product coming from a producer to a retailer and then to the end consumers. This channel is ideal for some businesses, such as clothing, toys, furniture, etc.
- Manufacturer↣ Retailer↣ End Consumers
- Two-Level Channel: In this channel, the wholesalers make bulk purchases from the manufacturer and send the products to the retailers to sell. Then the retailers sell the products to the end consumers. It is ideal for affordable and long-lasting products.
- Manufacturer↣ Wholesaler↣ Retailer↣ End Consumers
- Three-Level Channel: It entails a product coming from a manufacturer to an agent and then to a wholesaler. The wholesaler then divides the products into smaller packages to sell to retailers. The retailers then sell the products to the end consumers. In this case, agents assist with selling the products and getting the products delivered to the market quickly. This channel is suitable for high-demand products with a large target market.
- Manufacturer↣ Agent↣ Wholesaler↣ Retailer↣ End Consumers
Advantages and Disadvantages of Indirect Channel:
Here are some key advantages of indirect distribution channels;
- It allows a business to share its shipping and shortage costs.
- It reduces startup costs.
- Easy for customers to find your product in the market.
- Businesses can benefit from third-party’s experience, Salesforce, and infrastructure.
- The chances of expanding business are high.
- It allows companies to better focus on their core competencies.
- Instant process.
Indirect distribution channels also have some disadvantages;
- The effective cost of the product increases.
- Profit is also very low using this type of distribution system.
- It gives businesses partial control over how their product is marketed and sold.
- It includes the cost of hiring intermediaries.
- The delivery process is comparatively slow with this type of distribution channel.
Special Note: When a manufacturer uses both direct and indirect channels to reach the consumer, that is called a hybrid channel. Suppose a manufacturer sells its product online directly from its own e-commerce website. Besides that, they also have a relationship with an intermediary to distribute the same product in the market.
Functions Of Distribution Channel
The functions of the distribution channel are divided into three categories:
1. Transactional Functions:
Functions related to a transaction, such as buying, selling, and risk-bearing, are called transactional functions. The manufacturers sell products to intermediaries, who further sell them to the end consumers. In this way, products move from producer to consumer. With no buying and selling, there won’t be any transactional activities.
2. Logistical Functions:
The logistic function is to make sure that products must reach the market at the right place and at the right time to sell them to the consumers. This function involves the physical exchange of products, such as storage, shorting, packaging, transportation, etc.
3. Facilitating Functions:
Facilitating service basically involves after-sales services, financing, maintenance, channel coordination, information dissemination, etc.




