Emotional Intelligence: Definition, Skills, Testing, Benefits, Relation to management & Leadership [PDF Included]
The term Emotional Intelligence (EI) is very new to most people as the term itself came into existence a few decades back. However, its concept is known to people from as early as Socrates. Even Socrates explained emotional intelligence without knowing the term. Emotional intelligence falls under both business as well as psychological studies. The increasing popularisation of EI in recent times has drawn much attention and is being used extensively in the professional world along with the personal world for its intrinsic benefits. It affects our daily life and thus, it has become a very vital topic to study and research upon.
What you are going to learn?
Definition
Emotional Intelligence (EI) is the learned or innate ability to perceive, understand, use, manage and control our own emotions as well as the emotions of others in positive ways to have greater mental health, better job performance, effective communication, empathy, and leadership skills.
In 1990 two professors of psychology, Peter Salovey and John Mayer published their path-breaking article, named “Emotional Intelligence”, in the journal “Imagination, Cognition, and Personality” where the first academic attempt was made to inquire about and understand the term. In their words, Emotional Intelligence is “the ability to monitor one’s own and other people’s emotions, to discriminate between different emotions and label them appropriately, and to use emotional information to guide thinking and behavior”.
Thus, Salovey and Mayer’s model of Emotional Intelligence is composed of four key branches:
1. Perceiving emotions in oneself and others accurately through verbal, facial, emotional, and postural expressions.
2. Using emotions to facilitate thinking, judgment and memory.
3. Understanding emotions, feelings, emotional language, and the signals conveyed by emotions– for analyzing, labeling, and discriminating between feelings, and appreciating the outcomes.
4. Managing emotions by own self in order to achieve desired outcomes.
Emotional Intelligence Skills
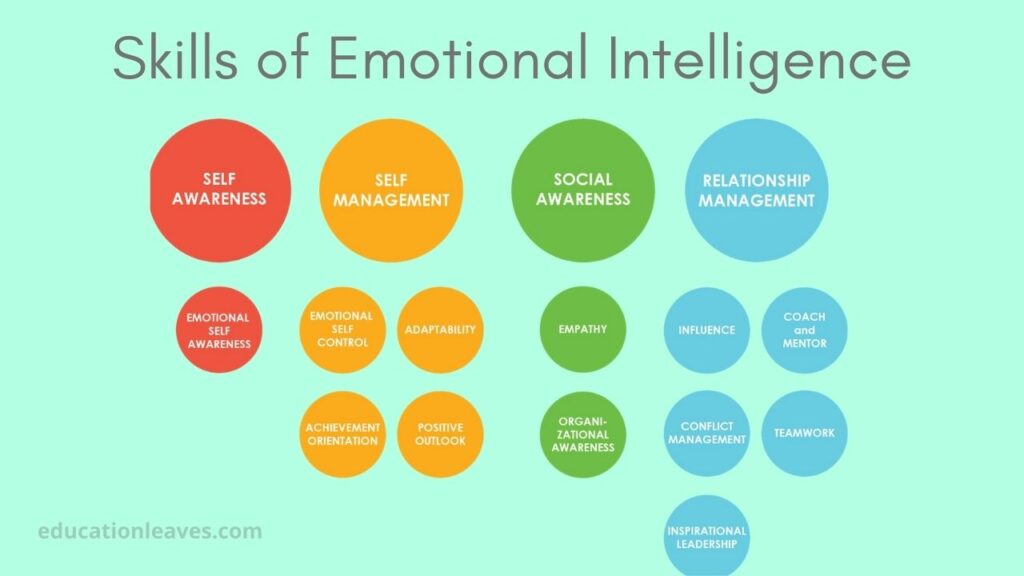
Based on Salovey and Mayer’s four-branch model of emotional intelligence a famous researcher, Daniel Goleman discussed five essential skills of emotional intelligence in his book ‘’Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ’’ (1995). Let us have a look at these skills or components of EI which serve as the foundation of the present Organisational Leadership Skills course.
1. Self-Awareness
This skill is based on the perception of emotions. It means recognizing and having a clear understanding of one’s own emotions, beliefs, strengths, and limitations. We can recognize, understand and manage the emotions of others only when we are aware of ourselves.
It allows us to correctly identify the impact of our emotions, actions, and moods on ourselves as well as others. We can build better personal as well as professional relationships, have stronger communication, improve our decision-making skills, manage conflicts effectively and motivate others. We can also get to know our weaknesses and also find a chance to improve them for our betterment. People with self-awareness are usually open to new information and experiences, have a good sense of humor, and are confident in themselves and their abilities.
Ways to improve self-awareness are–
- Journaling
- Paying attention to our own thoughts and emotions
- Learning new skills
- Asking for constructive feedback
- Practicing mediation and mindfulness
- Reflecting on our experiences
- Setting goals
- Pursuing our passions
- Developing the habit of positive self-talk
- Having a growth mindset
2. Self-Regulation
It deals with the ability to manage and control emotions, behaviors, and impulses. It simply means to pause, think and wait for the right time and place to express our emotions appropriately. People with strong self-regulation skills are flexible and can adapt to any change. Being thoughtful in nature they can manage difficult situations very well and can influence others to attain specific goals. They tend to take initiative, be committed, and hold themselves responsible for their own actions.
We can improve self-regulation by :
- Being mindful of our thoughts and feelings
- Building distress tolerance skills
- Finding ways to manage difficult emotions
- Looking at challenges as opportunities
- Practicing communication skills
- Recognizing that we have a choice in how we respond
- Using cognitive reframing to change thought patterns and emotional responses
- Working on accepting our emotions
3. Social Skills
The ability to interact well with others is another critical emotional intelligence skill.
Social skills include a wide range of relationship and interpersonal skills which cover active listening, verbal communication skills, nonverbal communication skills, leadership, persuasiveness, conflict management, as well as teamwork.
These skills help a lot on a personal level. Enhanced self-esteem and confidence can be gained which in turn help in greater understanding and acceptance of the emotions of ownself–facilitating easier positive personal dialogue. On a broader level, it is easy to talk to people having social skills as they become good listeners and trustworthy to share thoughts and opinions. Such people naturally become more charismatic and attractive to others as they tend to build meaningful relationships owing to a stronger understanding of themselves and others.
For instance, in a professional setting, managers, as well as workers, benefit by being able to build better relationships and connections and develop a strong rapport with each other.
Social skills can be improved by :
- Active listening
- Asking open-end questions
- Finding icebreakers to start conversations
- Noticing other people’s social skills
- Maintaining eye contact
- Notice other people’s social skills.
- Practicing good eye contact.
- Show interest in others.
- Practicing own social skills
- Watching and monitoring body language
4. Empathy
It is the ability to detect, define and understand the needs, emotions, and feelings of others and to be able to perceive their concerns and experiences through active interest and imagination. It is perhaps the most important element of emotional intelligence today because it serves as the link between self and others. It helps us to understand someone’s experiences in such a way as if we ourselves are feeling those experiences along with them.
According to Tim Minchin, empathy is a skill that can be improved by working upon it. He believes that empathy is an interpersonal skill that at some level comes naturally to most people. However,
Daniel Goleman has bracketed five essential elements of empathy:
- Understanding others— perhaps this is the shortest way to define empathy. Goleman says that by “sensing others’ feelings and perspectives and taking an active interest in their concerns” we can understand others and empathize with them.
- Developing others to their full potential by acting on their needs and concerns. This can be done by rewarding and praising them as well as providing them with constructive feedback, mentoring, coaching and assignments.
- Having a service orientation means prioritizing the needs of customers, genuinely understanding them, and going the extra mile to improve their satisfaction and loyalty. It is primarily aimed at work situations and may help in developing a long-term relationship between customers and the organization.
- Leveraging diversity should not be understood as treating everyone in exactly the same fashion but tailoring the way we interact with others to fit with their needs, feelings, and emotions. This skill helps in viewing diversity as an opportunity to work much better by respecting and relating well to everyone, regardless of their background.
- Political awareness is about understanding the power relationships and undercurrents, or hidden agendas, in an organization. Although it is considered manipulative at times, if used well and wisely, then political awareness becomes a force for good that helps individuals to navigate organizational relationships effectively, and the organizations get their work done.
Although empathy can often be difficult to achieve, the following ways can be implemented to develop empathy in someone:
- Listening to others
- Acknowledging and respecting the feelings of others even during disagreement
- Avoid making judgemental, belittling, or rejecting comments or statements
- Be willing to share your own feelings
- Asking questions to others to know more about them
- Talk to new people to gain new perspectives
- Try to imagine yourself in someone else’s place
- Engaging in a cause such as a community project
5. Motivation
Motivation refers to the ability to inspire both own self and others to improve, set goals, take initiative, accept challenges, stay committed to the goals, and stay optimistic during turbulent times. Self-motivated leaders have a high personal drive to hit the organizational milestones and fulfill their own inner needs and goals rather than making monetary achievements. Such leaders are generally action-oriented and are always ready to act on opportunities. They try to make the best use of time and avoid making unreasonable demands.
Motivation generates positivity and confidence in the leader, which overflows to the team as well. The motivated and empowered employees try to work to their potential, helping the organization to achieve collective goals.
Ways to improve motivation are:
- Setting small and measurable goals to build intrinsic motivation.
- Introducing challenges to keep things interesting.
- Celebrating the outcomes and reassessing the failures to get success in the next attempt
- Working with a friend or co-worker to find accountability.
- Avoid overusing extrinsic rewards.
Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
Leadership is a vital management function as it harnesses individual efforts towards the advancement of a collective goal for an organization’s success. Thus, leaders must have a clear and solid understanding of their own emotions and their impacts on both themselves and others. Emotional Intelligence is a must for the success of the leader, his/her team as well as the organization. Let us understand the relationship between emotional intelligence and leadership on the basis of the following 5 elements:
1. Self-awareness
A self-aware leader is always aware of his feelings, emotions, and actions and how these can affect the people around him. It also implies that the leader has a clear picture of his strengths as well as weaknesses. So, this can help the leader to exercise his personal traits appropriately for the benefit of the organization.
2. Self-regulation
It is all about regulating one’s own emotions and also understanding and controlling others’ emotions to obtain the desired result. In the case of leaders, self-regulation prevents them from making rushed and careless emotional decisions, stereotyping people, or compromising values. They rarely attack others verbally and control situations with calm and composure. They examine a code of ethics and hold themselves accountable when something goes wrong without blaming others in a team.
3. Motivation
Self-motivated leaders usually have high work standards for themselves and work consistently towards their goals. Leaders with high emotional intelligence can recognize the capability of their employees and colleagues and can motivate them to work to the best of their potential.
4. Empathy
Through empathizing with others a leader can put himself in someone else’s shoes. He can build a positive work atmosphere by being a good listener when the team needs, him and by providing them with appropriate responses and critical feedback. He can also challenge stereotypes and unfair assumptions, thus, earning loyalty and mutual respect from the team members.
5. Social Skills
A leader with excellent social skills can avoid a toxic workplace environment and can promote a healthy work culture through strategic conflict management, harmonizing human relationships, healthy collaboration and cooperation, effective communication, persuasiveness, and team leadership.
A leader can be technically skilled but if he or she lacks emotional intelligence then it can have severe consequences in the form of lower employee
engagement, higher turnover rate, and in turn, an unsuccessful career. Hence, emotional intelligence is very essential for leadership as leaders set the very tone of their organization.
Emotional Intelligence In Management
Emotional intelligence is relatively a new idea in the business world yet it has gained great momentum in the short span of time. Now effective running of a business organization is not possible without using emotional intelligence. EI helps organizations to improve organizational culture by enhancing employee acceptance changes, identifying transformational leaders, and creating more effective work teams.
Two American psychology researchers, Howard Gardner, and Thomas Hatch suggest that the following essential skills must be present in a leader for successful management:
- The ability to organize groups by coordinating the efforts of a network of people.
- The ability to mediate, prevent or resolve conflicts and negotiate solutions.
- The ability to empathize and communicate properly in order to establish better relationships with co-workers and colleagues.
- The capacity of perceiving feelings, motivations, and concerns of others for social analysis.
On one hand, emotional intelligence can be highly profitable for the organization. While on the other hand, the lack of EI can be destructive for a company due to the effects of bad morale, intimidation of employees, the arrogance of their leaders, bad atmosphere of work, decreased productivity, repeated mistakes, poor decision-making, and other such negative factors.
Impact of Emotional Intelligence
We can find a widespread interest in the area of emotional intelligence due to its increased beneficial effects. Here we shall discuss the impacts of EI on different factors:
1. Improved Performance at Work
Only technical skills and intellectual ability are not enough to achieve a successful career and life. Emotional intelligence is also required to excel in the career by navigating through the social complexities of the workplace, having better communication and coordination with co-workers, and leading and motivating others. Even the companies are using the Emotional Quotient (EQ) test before hiring their employees.
2. Physical Health Management
Uncontrolled emotions are proportional to uncontrolled stress, which in turn lead to serious health problems such as raised blood pressure, weakened immune system, increased risk of heart attacks and strokes, infertility, and accelerated aging process. Improving emotional intelligence can reduce stress levels and also prevent related health issues.
3. Mental Health Management
If emotions and stress are not controlled then it can affect the mental health also by causing anxiety and depression. Without proper management of stress levels, people have to struggle to form strong relationships. Or else they can feel lonely and
isolated which can cause further mental health problems.
4. Decreased Aggression Level
People with higher emotional intelligence possess a better understanding of their emotions and feelings along with their causes and consequences. They can control their anger, resolve conflicts strategically and thus display fewer aggressive behaviors such as anger or hostility.
5. Increased Positive Leadership
Improved emotional intelligence increases positive leadership by decreasing aggressiveness. Moreover, socio-emotional intervention programs aid in improving self-control of behavior, assertive behaviors, personal and social problem-solving, and the ability to analyze feelings of own self and others.
6. Enhanced Social Intelligence
Social skills help people to connect better with others and the world around them. The intelligence gained from these skills helps people in distinguishing friends from foes and achieve more confidence and open-mindedness. By employing social communication one can balance their nervous system by reducing stress and may feel loved and happy.
7. Better Relationships
Through self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and good communication skills we can get clarity in our thoughts and actions. We can express ourselves in a better way through effective communication. Good communication and clear understanding between people is very vital in building strong relationships, both in personal as well as professional settings. Motivating and active listening create an atmosphere of mutual trust among people. Thus, improved emotional intelligence can benefit in creating strong bonds and better relationships.
Testing Emotional Intelligence
Nowadays, companies are putting greater emphasis on emotional intelligence tests before hiring. These tests enable employers to identify their candidates’ personality, behavior, and inner qualities such as relationship management skills, leadership skills, teamwork, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. It is important to know what personality traits a candidate possesses in order to provide them the right positions.
A number of EI tests are developed in recent times although the science and methods behind them are still debated. The tests usually fall under two categories: 1) self-report tests, and 2) ability tests
Self-Report Tests
These are the most common types of tests as they are the easiest to conduct and score. These tests include a very simple method where respondents respond to the questions or statements by rating their own behaviors. However, the test-taker may not always agree with the responses.
Ability Tests
In these tests, people have to respond to given situations and then assess their skills. People are required to demonstrate their abilities which are rated by a third party.
However, there are other EI tests as well which are conducted by mental health professionals. Let us have a look at those tests:
Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT)
It is an ability test that calculates the four branches of Mayer-Salovey’s EI model. The test is basically an aptitude test that helps in finding out the leadership aspects and competency in an employee. From a global perspective, this test is flawed as it depends highly on culturally different “social norms”. Moreover, this test uses self-report tests, which are wholly based on personal perspectives, thus leaving scope for flaws in the results.
Emotional and Social Competency Inventory (ESCI)
The foundation of this type of test is an older instrument known as the Self-Assessment Questionnaire. It involves rating a person’s abilities in different emotional competencies, by the people who know him or her. This test helps in evaluating the social and emotional abilities of people in order to distinguish them as strong leaders.





Pingback: What is Exercise? 16 Benefits, 4 Types, and 7 Risks Associated with Exercise - EDUCATIONLEAVES