What is Production? 4 types of production, Factors of production, production function
The main goal of economic activity is to generate utilities for individuals. Production encompasses all activities within a timeframe that either yield utility during that period or enhance the society’s capacity to generate utility in the future. Understanding the specifics of production is crucial.
What you are going to learn?
What is Production?
Production is a process of value addition, which is developed to transform a set of input elements like man, raw material, capital, energy, information into finished products and services in proper quality and quantity.
In other words, Production is a process of combining various inputs (man, machine, material, money) in order to make something for consumption (product or services).
Significance of value addition in production can be transform row material into goods, assemble many small parts, or design a service. Production can be seen every day in factories, offices, hospitals, etc. Production can be agricultural, manufacturing, or service.Production plays a crucial role in the economy by creating goods and services that meet the needs and wants of consumers. It contributes to economic growth, job creation, and overall prosperity. Efficient production processes can lead to cost savings, increased competitiveness, and higher profits for businesses. By continuously improving production techniques and technologies, companies can stay ahead of the competition and meet the ever-changing demands of the market. Overall, production is a fundamental aspect of the economy that drives innovation, development, and progress.
Factors of production
The factors of production are the resources that are used to create goods and services. They are often referred to as the building blocks of the economy. Economists typically categorize these factors into four main groups:
Nature
Nature is a very important factor for any production. It is impossible to carry out production without land, water, and other resources. Suitable land and the availability of water make production easier.
Natural resources, such as oil and coal, can be extracted from the land and refined for production purpose consumption. Cultivation of crops on land by farmers increases its value and utility. Area, the shape of the production site, cost, drainage, and other facilities, the probability of floods, chance of earthquakes, etc. influence the selection of plant location.
Water is used for processing, drinking and sanitary purpose within a production site. Depending upon the nature of the plant water should be available in adequate quantity and proper quality.
In the production of leather, textile, etc. climate is an influencing factor. For such industries extreme humid or dry conditions are not suitable for production.
Labour
Human effort is a necessary factor for production. Skilled labour can make a significant difference in any production. Another important factor that influences plant location decisions is the availability of labour near the factory. The combination of an adequate number of labour with suitable skills and reasonable labour wages can highly benefit the production firm.
Labour by an uneducated and untrained worker is generally paid at low wages. Skilled and trained workers are referred to as human capital and they get paid at higher wages because they bring more than their physical capacity to the workplace. Hire skilled labour for their specific work increase the productivity of a production unit.
Capital
capital generally refers to money. But money is not a factor of production, because money is not directly involved with the production of product or services. Money used as a resource to buy capital goods like machine, equipment, raw materials etc.
It is important to distinguish between private capital and personal capital. Buying a car for personal use and family transport is not considers capital. But buying a vehicle for commercial uses considers as capital.
During a financial crisis or when they suffer losses, companies cut back on the capital expenditure to ensure profits. And, during periods of economic expansion, they invest in capital to purchase machinery and equipment to bring new products to market.
Enterprise
Enterprise is the activity that combines all the other factors of production into a product or service for the consumer market. Enterprise as a function involves in organizes other factors like applying government rules and regulation, working discipline within the production site, etc. into an operating unit. A good management team is greatly benefited in every business enterprise.
Understanding the factors of production is essential for understanding how economies function. These factors are all necessary for the production of goods and services, and they all play a role in determining the cost of production. The relative abundance or scarcity of each factor can also affect the types of goods and services that are produced in an economy.
For example, a country with an abundance of natural resources may be more likely to produce goods that are resource-intensive, such as oil or timber. On the other hand, a country with a highly skilled workforce may be more likely to produce goods that require a lot of labor, such as high-tech products.
The factors of production are also important for understanding how wealth is distributed in an economy. The people who own or control the factors of production are the ones who earn income from them. For example, the owners of land earn rent, the providers of labor earn wages, the owners of capital earn interest, and entrepreneurs earn profits.
Types of Production
There are four main types of production that are generally employed. Which type is suitable is decided by the nature of the product being produced, demand of the product on the market and supply of raw materials.
Four types of production are-
- Unit or Job type Production,
- Batch Production,
- Mass Production,
- Continuous Production or process production.
Let’s discuss each type separately,
1. Unit or Job type Production
Production in the form of Unit or Job production is predominantly evident when the focus is on creating a single unit of a product at a time. An illustrative instance of Job production is bespoke garments tailored specifically to your measurements or a customized cake crafted to your exact preferences.
This mode of production heavily relies on the expertise of the laborer. The emphasis is on manual labor rather than mechanized processes due to the unique nature of each product. Customer service holds significant importance in Unit or Job production.
2. Batch Production
Batch production is commonly utilized in consumer durables, FMCG, or similar industries with a wide range of products and varying demands. It occurs in batches, with the manufacturer determining the quantity of units to be produced in a single batch.
Examples of batch production include FMCG items like biscuits, confectioneries, and packaged foods. It is also prevalent in the pharmaceutical, hardware, and consumer durables sectors.
Since batch production is carried out in batches, interrupting the process once it has started can result in significant costs for the company. Demand and supply dynamics are crucial in batch production, with product seasonality heavily influenced by demand.
3. Mass Production
Mass production, also known as flow production or assembly line production, is a common type of production system used in the automobile industry and other industries requiring continuous production, such as the manufacturing process adopted by Ford Company.
An assembly line or mass-production plant is typically designed for specialized product manufacturing, with multiple workstations installed through which the assembly line progresses. Each workstation is responsible for a single type of work, making the process efficient and the overall assembly line productive.
Market demand does not significantly influence mass production, as the production capacity of the company is crucial for its success. Mass production necessitates a substantial initial investment and working capital.
4. Continuous Production or process production
There are many similarities between mass production and continuous production. They can be distinguished by the level of mechanical involvement. In mass production, both machines and humans collaborate, whereas in continuous production, machines carry out most of the work. Continuous production operates around the clock, 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.
Brewing serves as an example of continuous production. In brewing, production occurs continuously throughout the year, requiring significant time and attention.
Once production commences, it must continue without interruption to avoid substantial losses. Therefore, a controlled environment is essential for continuous production.
Production Function
The production function is the expression of the number of variables like raw materials, their quantity, number of machinery, the number of finished products, etc.It shows how these variables are combined to produce a certain level of output. By understanding the production function, businesses can optimize their production processes to achieve maximum efficiency and output.
A production function thus involves a wide range of activities from the plant location to the packing of products to be distributed by the marketing division of the organization. More experienced marketing division demand will more, thus production will be increased.The organization must ensure that all aspects of the production process are running smoothly in order to meet the demands of the marketing division. This includes efficient resource allocation, quality control measures, and timely delivery of products to the market. Failure to do so could result in lost sales and damage to the company’s reputation.
The modern evolution of the production function started with the industrial revolution in western countries and North America. New machinery was developed which helps in starting new and big industries.This led to increased productivity and efficiency in production processes, allowing for higher output levels and economic growth. The production function continued to evolve with advancements in technology, such as automation and computerization, further improving the efficiency and output of industries. Today, the production function is a key concept in economics and business, guiding decision-making processes and resource allocation strategies for organizations around the world.
various factors like labour charges, lack of skilled labour, etc led to automation. The first stage of the evolution of automation is Detroit Automation, the second stage is feedback control, and the third stage is Computer technology.The Detroit Automation stage saw the introduction of automated assembly lines in the automotive industry, drastically increasing production efficiency. Feedback control further enhanced automation by allowing machines to adjust their operations based on real-time data. Computer technology revolutionized automation by enabling complex tasks to be performed with precision and speed. These three stages collectively paved the way for the modern era of automation, transforming industries and increasing productivity worldwide.
The selection of plant location and plant layout is always difficult. The location of the plant should be in such a place where resources are easily available and have low distribution costs. A good plant layout permits the material to move little and at minimum cost.The layout should also ensure smooth workflow and efficient utilization of space. Proper planning and consideration of various factors such as production process, machinery placement, and employee convenience are crucial in determining the most suitable plant layout. Ultimately, a well-designed plant location and layout can significantly impact the overall productivity and success of the manufacturing operation.
Production, planning, and control consider the determination and regulation of the production processes and functions like routing, scheduling, dispatching, etc.These activities are crucial for ensuring that production runs smoothly and efficiently, meeting quality standards and deadlines. Production planning involves determining what needs to be produced, how much, and when, while control focuses on monitoring and adjusting production processes to ensure they are running as planned. Effective production, planning, and control are essential for optimizing resources, reducing costs, and maximizing productivity.
Another important function is Research and Development. Research means a critical investigation to acquire new knowledge and applied it to explore facts and information for the practical problem. The development comes after applied research. Development involves the design and fabrication of new or modification of products and then testing them.
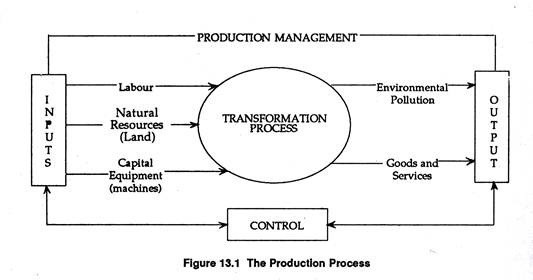
What is the Production process?
The production process is the entire flow of activities that transforms raw materials and resources into finished goods or services. It’s the heart of any business that creates products or delivers services. Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects:
Conversion of Inputs to Outputs:
- Inputs: These are the resources required to produce goods or services. They can be categorized into the four factors of production:
- Land (natural resources): minerals, oil, forests, water
- Labor: human effort, both physical and mental
- Capital: man-made resources like buildings, machinery, and equipment
- Entrepreneurship: the human spark that combines the other factors to create something new
- Outputs: These are the final products or services delivered to the customers.
Stages in Production:
While the specific stages can vary depending on the industry and product complexity, a general framework for the production process often includes:
- Design and Planning: This involves conceptualizing the product or service, creating blueprints, and outlining the production steps.
- Sourcing and Procurement: Raw materials and other necessary inputs are obtained from suppliers.
- Manufacturing/Operations: Here, the physical or service-based production activities occur, transforming inputs into the desired output.
- Quality Control: Products or services are inspected to ensure they meet the required quality standards.
- Packaging and Labeling: Products are prepared for storage, transport, and sale.
- Delivery and Distribution: Finished goods or services are delivered to customers or retailers.
Types of Production Processes:
There are three main categories of production processes based on the volume and variety of outputs:
- Mass Production: This is suitable for high-volume production of identical units, often on assembly lines. Cars, electronic goods, and soft drinks are some examples.
- Batch Production: This involves creating batches of similar products, with the possibility of switching between different items within the batch. Bakeries, furniture makers, and pharmaceutical companies often use batch production.
- Job Production: This caters to unique customer requirements, with production customized for each project. Examples include building ships, architectural projects, and high-end furniture.
Importance of the Production Process:
An efficient production process is crucial for businesses to succeed. It helps in:
- Cost Management: Optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste lead to cost reductions.
- Quality Control: Consistent quality ensures customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
- Productivity: Streamlined processes enhance output and efficiency.
- Meeting Customer Needs: Production flexibility allows businesses to adapt to changing customer demands.
By understanding and continuously improving the production process, businesses can gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Terms Related to Production
Product Planning
Product planning is the evaluation of the range, specification, and pricing of new and existing products according to the present and future market requirements and competition. Planning of the product is to satisfy the company objectives and to specify the required research, design, and development support.
In the planning activity, both existing and new products must be included and it follows the activity itself should deal with the proper balance between old and new products. Read more >>
Product Design
Before starting to manufacture a new product or improve a product, it is essential to design the product first. When a new idea has been conceived and developed to the point at which it shows itself to be both technically and commercially stable, it considers how the product should be made, Factors affecting product design, etc. Read more >>
Production Planning and Control
Production planning and control is a process that plans, manages, and controls the allocation of human resources, raw materials, and machinery to achieve maximum efficiency.
Production is the transformation of raw material into finished goods. planning looks ahead and anticipates possible problems then decides in advance as to how the production is carried out in the best way. Control makes sure that the programmed production is constantly maintained. Read more >>
Conclusion
The production process is the backbone of any business that creates products or delivers services. It’s a meticulously crafted dance transforming raw materials and resources into the finished goods or services we rely on daily.
Key Takeaways:
- The process efficiently converts inputs like labor, capital, and natural resources into desired outputs.
- It typically involves stages like design, sourcing, production, quality control, packaging, and delivery.
- Businesses can choose between mass production for high-volume identical items, batch production for similar items in smaller quantities, or job production for customized projects.
The Power of Optimization:
An optimized production process is a powerful tool for businesses. It allows for:
- Reduced Costs: By minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization, businesses can keep production costs under control.
- Enhanced Quality: Consistent quality control ensures customers receive products or services that meet expectations.
- Improved Productivity: Streamlined workflows lead to increased output without compromising quality.
- Customer Satisfaction: Flexibility in the production process allows businesses to adapt to changing customer needs.
Looking Ahead:
As technology and competition evolve, the production process will continue to adapt. Automation, digitalization, and a focus on sustainability are all shaping the future of production. Businesses that continuously strive to improve their production processes will be well-positioned for success in the ever-changing marketplace.





Pingback: What is Product Planning? Elements of Product Planning, Advantages of Product Planning - EDUCATIONLEAVES
Pingback: What is a Product Life Cycle? 4 Stages in a Product Life Cycle, Examples - EDUCATIONLEAVES
Pingback: Cost Control - Definition, Meaning, Differences between Cost control and Cost reduction - EDUCATIONLEAVES
Pingback: What is Group Purchasing Organization (GPO)? types, working, Pdf - EDUCATIONLEAVES
Pingback: What is Operations Management? (PDF included) Definition, Responsibilities, Nature, and Benefit of OM - EDUCATIONLEAVES
Pingback: What is Cost Accounting? [PDF Inside] Types, Objectives, Functions, Benefits, and Negatives, Financial Accounting - EDUCATIONLEAVES